Laser cutting has revolutionized industries from manufacturing to art. Its precision and versatility have made it a sought-after technology. From intricate metalwork to custom-made crafts, the laser-cutting machine offers endless possibilities. This blog will delve into the science and technology behind laser cutting, the benefits of laser cutting, how a laser cutting machine works, and its diverse applications.
What is Laser Cutting?
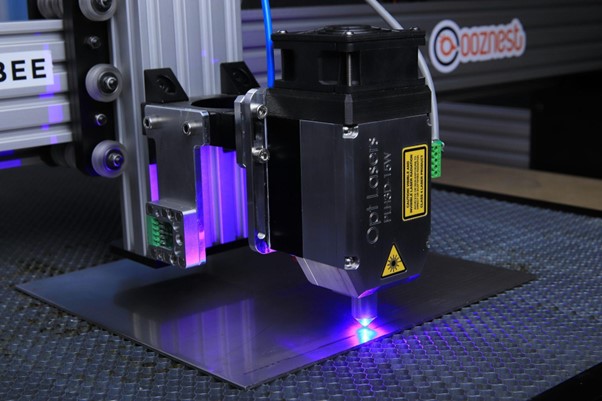
Laser cutting is a manufacturing process that uses a laser cutting machine, which further emits a focused laser beam to cut through materials. It’s used for precision cutting of various materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. Unlike traditional cutting methods, laser cutting offers high precision, minimal waste, and the ability to cut complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible with other techniques.
The Fundamentals of Laser Technology
What is a Laser?
LASER stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Laser technology works by exciting atoms in a material, causing them to emit light in a specific wavelength. This light is amplified through a process called stimulated emission, resulting in a concentrated beam of light with a single wavelength.
Types of Lasers Used in Cutting
Common laser types for cutting are CO2 lasers, which are suitable for non-metals like wood, acrylics, and textiles. Fiber lasers are ideal for cutting metals, especially stainless steel, and aluminum, due to their efficiency and speed, and Nd lasers are known for their versatility to cut metals and non-metals while balancing the power and accuracy of the cut.
How Laser Cutting Works
1. Laser Generation
Lasers generate high-intensity light by exciting gas or solid-state materials. This excitation causes atoms to emit light, which is amplified through stimulated emission, resulting in a concentrated beam of light with a single wavelength.
2. Beam Focusing
Lenses play a crucial role in laser cutting by focusing the laser beam on a small point. This concentration increases the intensity and heat of the beam, allowing it to cut through materials efficiently and precisely. The choice of lens depends on the desired beam size and cutting depth.
3. Material Interaction
The focused laser beam interacts with the material in several ways:
Melting
The intense heat from the laser can melt the material, creating a molten pool.
Vaporization
If the temperature is high enough, the material can be vaporized, turning it into gas.
Thermal cutting
The heat generated by the laser causes the material to expand and contract, creating stress that eventually leads to the material fracturing and separating.
4. Assist Gases
Assist gases like oxygen or nitrogen are used to improve cutting efficiency and quality. Oxygen accelerates the cutting process by oxidizing the molten material, while nitrogen helps prevent oxidation and maintains a stable cutting environment.
Advantages of Laser Cutting
Precision and Accuracy
The focused laser beam can create highly detailed cuts that are difficult or impossible with traditional methods like sawing or shearing. This precision is essential for applications requiring intricate details and tolerances.
Versatility
Laser cutting is versatile, handling a wide range of materials like:
- Metals: Stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper
- Wood: Various types, including hardwoods and softwoods
- Plastics: Acrylic, polycarbonate, ABS
- Fabrics: Leather, textiles, and other materials
Minimal Waste
Unlike traditional cutting methods, laser cutting can produce intricate shapes with minimal kerf (the width of the cut), reducing material loss and improving efficiency. This is especially beneficial for valuable materials or complex designs.
Speed
Laser-cutting machines offer rapid processing speeds, allowing for efficient production and shorter turnaround times. This increased productivity can benefit businesses by meeting deadlines, increasing output, and improving overall efficiency.
Applications of Laser Cutting
Manufacturing
Its precision and versatility allow for the efficient and accurate cutting of complex shapes and materials used in these sectors, contributing to the production of high-quality and durable components.
Fashion and Textiles
Laser cutting enables intricate designs in clothing and accessories. Its precision allows for complex patterns, perforations, and embellishments. This technology is used to create unique and stylish pieces, adding value and visual appeal to fashion items.
Signage and Branding
Laser cutting offers precision and versatility for creating customized signs and promotional materials. It enables intricate designs, precise cuts, and a wide range of materials, making it ideal for producing unique and eye-catching promotional pieces.
Art and Craft
Artists and crafters use laser cutting to create unique pieces. From intricate jewelry and sculptures to custom-made home decor, laser cutting enables precision and detail, opening up new possibilities for artistic expression and creativity.
If you need any type of assistance regarding laser cutting, then feel free to contact Max Laser, and their team will help you out.
Conclusion
Laser cutting is a versatile and precise technology whose science is essential to understand. You can further explore applications in multiple industries and consider benefits for your projects accordingly.
Article Provided